Table of Contents
Sater Frisian in Germany
Language designations:
Language vitality according to:
Click here for a full overview of the language vitality colour codes.
Linguistic aspects:
- Script: Latin
Language standardisation
Two linguists stand out in the language standardisation of Sater Frisian, namely, Pyt Kramer and Marron Fort. West-Frisian Pyt Kramer has developed the Seelter Woudebouk (Sater Frisian dicionary) from Sater Frisian to both West Frisian and German, published in 1961, and the Näi Seelter Woudebouk, A-E (New Sater Frisian Dictionary, A-E) in 1992. Moreover, he has written the Kute Seelter Sproakleere (short grammar of Sater Frisian), published in 1982 and 1996. The American linguist Marron Fort collected words while doing linguistic research over a span of 20 years in Saterland, and with this collection, he created a Saterfriesisches Wörterbuch (Eng: Sater Frisian dictionary), published in 1980, which later was published online and as app.2) The work of Fort is also used as reference for school materials.3) The Seeltersk Kontoor has an additional wordlist to expand the vocabulary not covered in these dictionaries of Kramer and Fort. Words are introduced by the Saterland schools, Sater Frisian associations, work groups, etc. 4)
In the period of 2021-2023, Linguistics and Grammar of Sater Frisian have been described, intended for, among others, linguists and the Saterland language community.
Demographics
Language Area
Sater Frisian or Seeltersk is spoken in four villages in the municipality Saterland, within the district Cloppenburg, the state of Lower Saxony. These villages are Strücklingen (Strukelje), Ramsloh (Roomelse) and Scharrel (Skäddel) and Sedelsberg (Sedelsbierich). It was marked as the smallest “language island” in Europe according to the Guinness Book of Records in 1991.5)
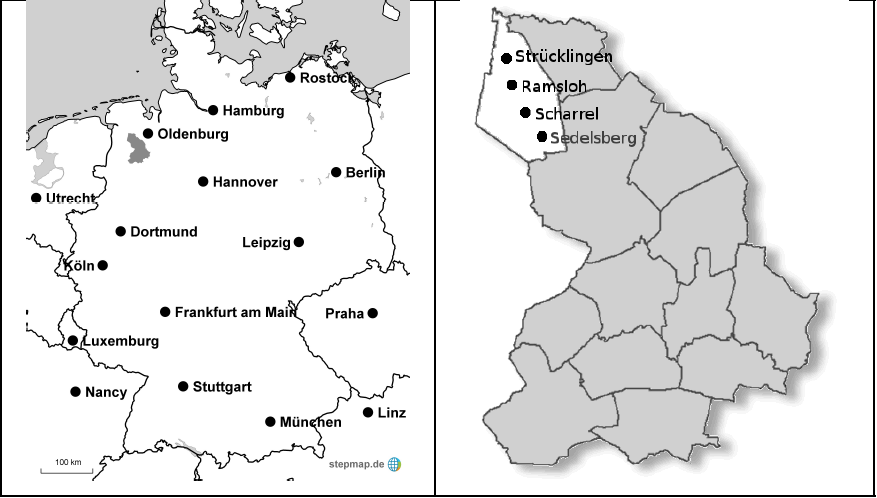
The map shows the location of Saterland. On the left, the district of Cloppenburg is marked in grey within Germany, and on the right, Saterland and the four villages are shown within Cloppenburg.6)
Saterland lay quite isolated, as it was surrounded by boggy moorland, and could only be reached via boat or in a dry spell up unto the start of the 19th century.7) In the 19th century, the number of Lower German speakers expanded in Saterland, and in the 20th century, High German became more and more dominant, also due to emigrants of German descent. 8)
Sater Frisian is one of the three Frisian languages alongside West Frisian and North Frisian. Sater Frisian is the only variety of East Frisian alive today. 9) The status of Sater Frisian as language or dialect was a point of discussion, because of its small number of speakers, and debate whether it belonged to the Frisian or German language families. 10) It is now recognised as a minority language. The four main villages where it is spoken have mutually intelligible dialects. 11)12)

The map shows the areas where West Frisian (dark blue), East Frisian (light blue) and North Frisian (blue) are spoken 13)
Speaker numbers
Estimates of speaker numbers vary between a 1000 and 2000, with some as high as 5000 (worldwide).14)15)16)17) Stellmacher (1998) conducted a study with his students in 1995, and the results showed that 4.058 people claimed that they understood Sater Frisian, and the number of active speakers was around 2.250, wich would be almost as high as a hundred years earlier (2.500)18) Though the absolute number of speakers remains relatively stable, the relative number decreases within Saterand, with 85% of the population who could speak the language around 1850, 50% in 1950, and 20% at the end of the 20th century. 19) The relative numbers of speakers varies from village to village, with the lowest percentage in Sedelsberg. 20)
Sater Frisian has lost ground as a family language in favour of Low German of High German, and often, High German was spoken to counter presumed disadvantages at school to have Sater Frisian as first language. Nowadays, a decline in knowledge can be seen with the younger speakers.21)
Education of the language
History of language education:
In 1800 already, the use of Sater Frisian in education was advocated for (instead of High German) by Johann Hoche, as he believed the language would support pupils to learn, however, Sater Frisian was not incorporated in education until almost two centuries later, in the 1990s. 22)
In 1994, the Seelter Buund initiated the project Seeltersk in dän Bäidenstuun (Eng: Sater Frisian in the Kindergarten) to include Sater Frisian in pre-school education, run by volunteers. In 1999, Sater Frisian was recognised via the European Charter for Regional and Minority languages, with undertakings for pre-school education and university/higher education. In 2000, it was reported that, for one hour per week, Sater Frisian was used (with consent of legal guardians) with children attending the five nursery schools within Saterland. 23)
Sater Frisian was not present at all in primary schools in 1988, although people would have supported it. 24) In 1996, it was reported that Sater Frisian was offered for two hours a week in primary school, and no audiovisual teaching materials were available. 25). In 1998, the Lower Saxon school act allowed to include Sater Frisian in education after pre-school. In 2010, the model project Das Saterland als Modellregion für frühe Mehrsprachigkeit (Eng:The Saterland as a model region for early multilingualism) was initiated. This project aims to educate (pre-)school teachers in the Sater Frisian language so that they can pass it on. 26) Since January 2012, there are opportunities to have Sater Frisian included in certain classes as language of instruction in primary and secondary school (with consent legal guardians).27)28)
In pre-schools, primary schools or secondary schools, the presence of Sater Frisian vary per school in Saterland, as schools are faced with challenges such as lack of teaching staff, class sizes, restrictive legal requirements, or the COVID-19 pandemic when classes in Sater Frisian were discontinued. 29)30) 31)
Legislation of language education
Legislation on European Level
European Charter for Regional or Minority languages
Sater Frisian is covered by the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages (ECRML) under Part II and Part III in Niedersachsen (Lower Saxony) since 1999. It encourages the use of Sater Frisian in pre-school, tertiary and adult education, as in Article 8, it recognises to:
- 1.aiv: favour/encourage the provision (or a substantial part) of pre-school education;
- 1.eii: provide facilities for the study at tertiary level;
- 1.fiii: favour/encourage the subject in adult/continuing education;
- 1.g: ensure the teaching of the history and the culture;
- 1.i: set up a supervisory body
In the 2022 report, the Committee of Experts considered a few undertakings had deteriorated, including those concerning pre-school education (marked “not-fulfilled”) and tertiary education (marked “partly-fulfilled”). 32) It therefore makes the following recommendations to: “[e]ncourage the provision of at least a substantial part of pre-school education in Sater Frisian and strengthen the educational offer for Sater Frisian at all appropriate levels,” and to “[s]et up a supervisory body responsible for monitoring the progress achieved in the teaching of Sater Frisian and for drawing up public periodic reports of its findings” (p.43). 33)
Framework Convention for the Protection of National Minorities
Germany has signed and ratified the Framework Convention for the Protection of National Minorities, which has been in force since 1998. With it, Germany recognised
the national minorities of the Danes, of the Sorbian people and of the German Sinti and Roma, and the ethnic group of Frisians in Germany. 34)
In the 2022 opinion, the Advisory Committee of the Framework Convention encouraged “ the authorities to further expand the offer of Sater Frisian teaching in day care centres, schools and at university” (p.33). 35)
Legislation on national level
In Germany, four national minorities are recognised: the Frisians, the Danes, the German Sinti and Roma, and the Sorbs. Among the Frisians are the North Frisian and East Frisians (among them, Sater Frisians). 36)37)
The German school system is governed by the federal principles of the state, and each state is responsible for its educational system.
Legislation on Local Level
Lower Saxony School Act
In 1998, Lower Saxony adopted the Niedersächsisches Schulgesetz (Eng: Lower Saxony School Act) There, it is stated that pupils should be able to develop their possibilities further extend their language skills gained before school, and to understand, perceive and express, including the relevant regional form of Low German or Frisian.38)
The Region and its Languages in Education
In 2011, Lower Saxony adopted the Die Region und ihre Sprachen im Unterricht (Eng: The Region and its Languages in Education). It promotes the continious inclusion and education of both Low German and Sater Frisian, and provides that primary schools and secondary schools (level I) can teach in Sater Frisian in selected subjects. Pupils who want to such classes, need approval of their legal guardians. 39)
In 2021, the Seelter Buund (Eng: Sater Association) expressed to the Comittee of Experts (ECRML) that this decree should be renewed, with a focus on hours of instruction and pupil numbers.40)
The Region and the Languages Low German and Sater Frisian in Education
In 2019, Lower Saxony adopted the Die Region und die Sprachen Niederdeutsch und Saterfriesisch im Unterricht (Eng: The Region and the Languages Low German and Sater Frisian in Education). Based upon the previous 2011 act, this act provides the opportunity for primary schools to teach Sater Frisian in selected subjects within the compulsory curriculum (with the exception of German and foreign languages). The lessons are offered bilingually or by immersion. This learning path can be continued in secondary school, where the acts also provides the opportunity to use Sater Frisian in elective courses, compulsory elective courses or in compulsory elective subjects (with the exception of other languages). For students to enroll classes in Sater Frisian, permission is needed from their legal guardian. The Lower Saxony State School Authority supports the schools with advice.41)
In 2021, the Seelter Buund expressed to the Comittee of Experts (ECRML) that the consent of legal guardians (both stated in Die Region und ihre Sprachen im Unterricht and Die Region und die Sprachen Niederdeutsch und Saterfriesisch im Unterricht) means that in some years, there are too few pupils for these bilingual lessons to take place due to a ministerial decree on minimal class sizes. The Seelter Buund therefore wishes for more flexible rules to accomodate these situations. 42)
Institutional support for education of the language:
Institutional support
The Seelter Buund aims to incorporate Sater Frisian in (pre-)primary schools, with the involvement of voluntary workers. They have been offering courses for adults as well.
The Seeltersk Kontoor, hosted by the Oldenburgischen Landschaft, operates in the fields of research, support, and emancipation of Sater Frisian language community, including political lobby work and project coördination. The office is coordinated by the scientific representative for Sater Frisian. In 2021, the Oarbaidskring Seeltersk (Eng: Sater Frisian Working group) was founded by the scientific representative for Sater Frisian, for active community members to meet and exchange ideas to initiate joint projects 43) In March 2023, the Seelter Buund wrote a letter to the Federal Ministry of the Interior to ask for the continuation of the position of the scientific representative for Sater Frisian, whose contract will end in November 2023. 44)
The Federal Ministry of the Interior has established the Minderheitensekretariat (Eng: Minority Secretariat), as a liaison office for the associations of the four national minorities with the federal institutions 45). The associations of these minorities are represented in the Minderheitenrat (Eng: Minority Council). 46) The Seelter Buund has a member in the Minority Council. The Minority Secretariat and the Minority Council represent the interests of the four minorities in Germany. 47)
Projects
In 2010, a project Seeltersk an do Skoulen in Seelterlound (Eng: Sater Frisian at the schools in Saterland) was initiated. This project strives for all primary school children to have the choice to have Sater Frisian as language of instruction except for the subjects of German and English, or to have the one hour subject Sater Frisian. For this project, teacher training in Sater Frisian was the first step, which was funded by the Niedersächsische Kultusministerium (Eng: Lower Saxon Ministry of Culture) and the Oldenburgische Landschaft, Universität Oldenburg and the Seelter Buund. 48).
In the period 2010/2012 to 2019, the model project Ostfriesland und das Saterland als Modellregion für frühe Mehrsprachigkeit (Eng: Ostfriesland and Saterland as a model region for early multilingualism) ran to promote early multilingualism and the use of Sater Frisian and Lower German in schools as language of instruction. For Sater Frisian, two primary schools were involved, namely Litje Skoule Skäddel and Marienschule Strücklingen. Overall, the project was well reveceived by the project initiators, coordinator, teachers and pupils. 49)
Language Learning materials
In 2015 and 2016, the learning materials Die Seelterfoaks – dät Bouk (Eng: The Sater Frisian fox -the book; 2015) and Seeltersk säikedät Säärm-moak-Bouk (Eng: The Sater Frisian fox - the do-it-yourself book; 2016) were publsihed, in which the mascot, the Sater Frisian fox, explores the language and history.50) 51)
In 2019/2020, a CD was produced, Sjung mäd uus (Sing with us), with Sater Frisian children's songs, sung by children.
In June 2022, the learning method Seeltersk lopt (Eng: Sater Frisian walks) for years 1-4 was presented. The methodology was developed by Ingeborg Remmers and Edith Sassen, is based on the Lower German Platt löpt version, provides teachers' instructions and audio, and aims to bring children to A2 level according to the CEFR. The state of Lower Saxony provided €40,000 for this methodology. 52) The Litje Skoule Skäddel and Seeltersk Kontoor have made it digitally available in 2023. 53)
To use learning materials at schools, they have to be approved by the Niedersächsisches Landesinstitut für schulische Qualitätsentwicklung, NLQ (English: Lower Saxony State Institute for School Quality Development). In 2023, the learning method Seeltersk lopt has been approved to be used. 54)
In the period 2023-2025, the four primary schools in Saterland introduced bilingual German/Sater Frisian signing in their buildings (see visibility of Saterfrisian), and at the start of the schoolyear of 2025-2026, all pupils of these schools received a Sater Frisian school planner, customised per school. 55)
Teacher support
Since 2009, students in teacher training at the University of Oldenburg can take courses on Sater Frisian, as part of the Low-German specialisation. 56)57) 58) Connected to this, the textbook Friesischer Sprachkurs : Seeltersk was published in 2011. 59) The Seelter Buund has expressed that higher education and teacher training institutions should work together concerning the training for (pre-)school teachers. 60) Since 2014, the NLQ offers Sater Frisian certificate courses, in cooperation with the Niedersächsisches Kultusministerium and university of Oldenburg.
Connected to the project Ostfriesland und das Saterland als Modellregion für frühe Mehrsprachigkeit, Sater Frisian courses were offered for the volunteers/teachers, with special attention to immersive lessons. 61) 62)63)
For Sater Frisian, ECRML Article 8.1h, that is 'to provide the basic and further training of the teachers […]' has not been ratified. Nonetheless, in 2022, the Committee of Ministers recommended, in general, to “ensure that a sufficient number of adequately trained teachers for regional or minority language education is available.” 64)
Financial support
The Seelter Buund receives around €2000 per year from the municipality of Saterland. The Seelter Buund is also responsible for the compensations for the people teaching Sater Frisian at pre-primary schools (the Seelter Buund can declare these costs at the municipalty since 2021). 65)66)
The Lower Saxony Ministry for Science and Culture provides funding for courses. In 2019, Lower Saxony provided €10,000 for two projects (total costs €29,000) to produce the CD with children's songs and extension of the app 'Kleine Saterfriesen'. In November 2020, Lower Saxony has provided financial support for the post of wissenschaftlicher Beauftragter für Saterfriesisch (Eng: scientific representative for Sater Frisian at the Seeltersk-Kontoor, at the Oldenburgische Landschaft. This representative aims to strengthen Sater Frisian with research, support, and emancipation of Sater Frisian language community. Since February 2023, a second staff member was appointed at Seeltersk-kantoor, for a year, to promote the use of the language and organise a conference in 2024. This second post is financed by the Oldenburgische Landschaft and the Fryske Akademy (Eng: Frisian Academy, Netherlands). 67)
Education presence
Pre-school education
Since 1994, the Seelter Buund has started a project Seeltersk in dän Bäidenstuun (Eng: Sater Frisian in the Kindergarten)) to include Sater Frisian in nursery schools with a weekly Sater Frisian activity group, which is lead by volunteers. In 2011, there were 140 children who attended the activity groups across the five nursery schools. 68) In 2021, the Seelter Buund reported that three out of six nursery schools routinely offer this activity group, and that the educational staff can be paid for their work, for the first time. 69)
There are several Bäidenstuune, nursery schools, where Sater Frisian has/had a place, f.e. with activity groups:
- Pusteblume in Roomelse, Ramsloh 70)
- Unterm Regenbogen in Skäddel, Scharrel 71)
- St. Jakobus-Bäidenstuun in Roomelse, Ramsloh 72)
- St. Marien in Seedelsbierich, Sedelsberg 73)
- St. Georg in Strukelje, Strücklingen
The new (2021) kindergarten Seelterfoakse in Roomelse, Ramsloh, also offers Sater Frisian, and is supported by the Seelter Buund and other kindergartens to set up the activity group 74)
In the 2022 report, the Committee of Experts considered pre-school education in Sater Frisian “not sufficient to represent at least a substantial part of education in this language” and therefore, consideres the undertaking “not fulfilled” (p.42).75)
Primary education
Since 1996, Sater Frisian is included on a voluntary base in primary schools of the municipalty Saterland, and schools can spend 265 hours per school year for teaching (about) the minority language 76). 77) In 2011, 150 children attended Sater Frisian class, ten years later, in 2021, 95 pupils attended Sater Frisian classes either in immersion lessons or activity groups.78). 79) Due to the COVIC-19 pandemic, there has been a suspension of Sater Frisian classes in 2020 and 2021.80) 81) The primary schools make use of the available learning materials.
Since early 2025, all four primary schools in Saterland offer Sater Frisian 82)83). These are:
- Litje Skoule in Skäddel / Scharrel, offers Sater Frisian in immersive lessons (year 1) and within an activity group (years 1-4)
- Marienschule in Strukelje / Strücklingen, offers Sater Frisian within an activity group (years 1-3), but no longer offers immersive lessons
- Grundschule Ramsloh in Roomelse / Ramsloh, offers Sater Frisian within an activity group (1 year)
- Astrid-Líndgren-Grundschule in Seedelsbierich /Sedelsberg, after an interval of 10 years due to the absence of a teacher, the school started the Saterfrisian activity group in 2025, with a teacher and a volunteer language assistant 84)85)
In three primary schools, the teachers are supported by language assistants. Language training for the assistance is offered by the Seeltersk Kontoor.
activity groups
On a voluntary basis (legal permission of the pupil's guardian), children can take part in activity groups at school (years 1-4), for one hour a week 86). These groups aim to support bilingualism, for children to become familiar with the language, and to increase the pupils' listening and speaking skills, with a lesser emphasis on reading and writing skills. This is done with themetic lessons, which concern e.g. seasons, clothing, pets, parts of the body, festivals, etc.87)88)
immersion lessons
On a voluntary basis (legal permission of the pupil's guardian), a school can offer immersion lessons. Two schools, namely Litje Skoule and Marienschule, have implemented such lessons, for example with mathemetics (5 hours a week) or music as immersive subject (1 hour a week).89) Nonetheless, there are issues to implement these immersive classes. Due to a lack of staff, the Marienschule no longer can offer this option, and the Litje Skoule cannot offer this when classes are too small and not enough pupils have consent of their legal guardians for these immersion lessons. 90)91) The Seelter Buund has expressed their concerns about teacher training, staff and the legal consent towards the Comittee of Experts (ECRML). Concerning class size and legal consent, the Seelter Buund wishes for more flexible rules to accomodate these situations. 92)
projects
Sater Frisian is also included and/or taught in school projects, activities or events, such as:
- Ostfriesland und das Saterland als Modellregionen für frühe Mehrsprachigkeit: In the period 2010/2012 to 2019, this project promoted early multilingualism and the use of Sater Frisian in schools as language of instruction. Two primary schools were involved, namely Litje Skoule Skäddel and Marienschule Strücklingen. 93)
- Lesewettbewerb (Eng: reading contest). A biennial reading contest is held, organised by the Oldenburgische Landschaft, in which several schools compete for the best reader (years 3 and 4). In 2023, the 29th edition of this competition is organised. 94) Several schools participate(d), e.g. Litje Skoule, Marienschule, Grundschule Ramsloh. 95)96)97)
visibility of Saterfrisian
Since April 2023, schools in Saterfriesland have made Sater Frisian more visible with inscriptions on the doors in the building. The Litje Skoule in Skäddel / Scharrel was the first 101), and the Astrid-Líndgren-Grundschule in Seedelsbierich /Sedelsberg was the fourth and last primary school to introduce bilingual signs 102).
Seelterfräiske Skoule
The two primary schools Litje Skoule and Marienschule have a certifite as Seelterfräiske Skoule (Eng: Sater Frisian school), for their outstanding and long-term services for Sater Frisian, handed out by the Niedersächsisches Kultusministerium. 103)104)
Secondary education
Sater Frisian can be taken as optional subject or in immersion, on a voluntary base, in secondary schools.105) There are two secondary schools in Saterland. Both partake in the Lesewettbewerb (Eng: reading competition). 106)107)
Haupt- und Realschule Saterland in Roomelse, Ramsloh offered Sater Frisian as voluntary subject at the Realschüle (type of secondary school, until year 10), but not at the Hauptschüle (type of secondary school, until year 9)108), but, due to a lack of teachers, this has been cancelled since 2016.109) One teacher organises a Sater Frisian activity twice a year, in the textiles programme of year 5.
Laurentius-Siemer-Gymnasium in Roomelse, Ramsloh offered an elective Sater Frisian course, but, due to a lack of teachers, this has been cancelled since 2018. 110) In June 2023, a guest lecture, an introduction to the language and history of Saterland, was given by the Seeltersk-Kontoor, in collaboration with the Oarbaidskring Seeltersk and the Seelter Buund111).
higher education/university education
At the Carl von Ossietzky Universität Oldenburg in Oldenburg course in Sater Frisian has been offered since 2009, for teacher students, within the Germanic department, with a specialisation in Low Saxon. 112) The university has also been involved in the project, Das Saterland als Modellregion für frühe Mehrsprachigkeit.113) In the 2022 report, the Committee of Experts considered the undertakings as “only partly fulfilled”, due to its place within the German studies and specialisation of Low Saxon (p.42).114)
Occasionaly, higher education institutes such as the Westfälischen Wilhelms-Universität in Münster and the NHL Stenden Hogeschool in Leeuwarden (the Netherlands) have offered Sater Frisian courses. 115)
Adult education
The Seelter Buund, in collaboration with Seeltersk Kontoor, organises beginner and advanced Sater Frisian courses. In 2023, these courses without a participation fee, as the Lower Saxony Ministry for Science and Culture provides the funding 116)
A Sater Frisian course is also offered at the Folks Volkshochschule für die Stadt und den Kreis Leer e.V (Eng: adult education centre for the region of Leer) 117)
Learning resources
Organisations
- Seelter Bund Organisation founded in 1952 for the promotion of Sater Frisian. Activities include language courses and community events.
- Seeltersk-Kontoor Organisation for the Oldenburgischen Landschaft for research, support, and emancipation of Sater Frisian language community, including political lobby work and project coördination, lead by the scientific representative for Sater Frisian. It also initiated:
- Seelter Oarbaids-Kring Sater Frisian Working group for active community members to meet and exchange ideas to initiate joint projects.
- Toal-Normierengs-Truppe (TNT): Language standardisation team to draw up thematic lists of words for the classroom.
- Fräiske Räid Frisian Council: umbrella organisation for Sater, West & North Frisian organisations.
Online resources
Linguistics, grammars, dictionaries
- Sprachlehre des Saterfriesischen 2022-2023 Linguistics of Sater Frisian 2022-2023 (German)
- Sprachlehre des Saterfriesischen 2022 Linguistics of Sater Frisian 2022 (German)
- Grammatik des Saterfriesischen Grammar of Sater Frisian (replaced by Sprachlehre des Saterfriesischen 2022-2023; German)
- Saterfriesisches wörterbuch online dictionary Sater Frisian ↔ German (by Fort)
- Seelter Woudebouk: Paat Seeltersk-Düütsk dictionary Sater Frisian ↔ German (by Kramer)
- Seelter Woudebouk: Seeltersk-Wäästfräisk dictionary Sater Frisian ↔ West Frisian (by Kramer)
- Neue Wörterliste Deutsch-Saterfriesisch: additional wordlist to expand the vocabulary not covered in the dictionaries of Fort and Kramer
- The digital collection by Pyt Kramer Sater Frisian dictionaries, wordlists and grammar.
- saterfriesischen Wörterbüchern viele Vogelnamen Bird names (German - Sater Frisian)
Learning materials
- Seeltersk lopt School books (2022) for years 1-4, including audio (Sater Frisian-German)
- Online Saterfriesisch lernen: Friesischer Sprachkurs Seeltersk Learn Sater Frisian online (German)
- Seeltersk - Kurs Saterfriesisch - Sater Frisian Course - Kursus Sóóterfräisk - Cursus Saterfries 15 lessons Sater Frisian (Dutch, English, German, West Frisian)
- Seeltersk lernen collection of learning materials
- lessons Seeltersk moaket klouk 2022 (Eng: Saterfrisian is cool): Thematic educational materials, concerning school, seasonal vegetables, and making waffles.
- Wimmelspiel: app for iOS and Android was created for 3 to 6 year old children as well as for adults to start learning Sater Frisian
- Kleine Saterfriesen: app for iOS and Android for 3-6 year old children for learning the language
- Seelterapps: practice materials for primary school students
Other
- Digitalisierung wissenschaftlicher Werke Digitalised scientific resources(English, German, Sater Frisian, West Frisian)
- Videos vom Saterfriesischbeauftragten Videos from the Saterfriesischbeauftragten about various aspects on the language and community (German, Sater Frisian, West Frisian)



