Table of Contents
Scottish Gaelic in the United Kingdom
Language designations:
- In the language itself: Gàidhlig
- ISO 639-3 standard: gla
Language vitality according to:
Click here for a full overview of the language vitality colour codes.
Linguistic aspects:
Language standardization:
Demographics
Language Area
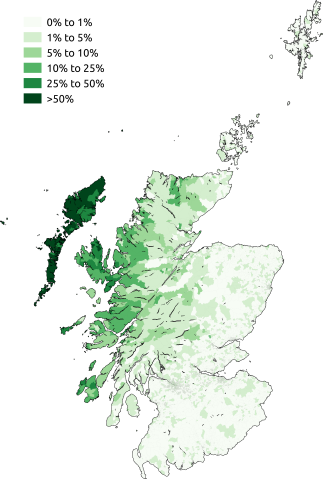
Gaelic is spoken mainly in the Highlands and Islands of Scotland. It is a Celtic language closely related to Irish and Manx, and more distantly related to Welsh, Breton and Cornish.
Map shows the proportion of respondents in the 2011 census aged 3 and above who stated that they can speak Scottish Gaelic. Map was created by SkateTier, and is licensed under CC BY-SA 3.0
Speaker numbers
- In 2011, about 158,000 Scots spoke Gaelic, compared to about 59,000 in 2001 1).
- This corresponds to 1.13% of the Scottish population, compared to 1.20% in 2001.
Language and education legislation
History of language education:
Gaelic-medium primary education was first introduced in the traditional heartlands of the language in the mid 1970's, and soon followed in the wake of Gaels who had migrated to urban and Lowland areas. Due to strong support from Scottish parents for Gaelic medium education, additional Gaelic-medium schools were opened, and in 1999/2000, 59 Gaelic-medium schools existed throughout Scotland. 2)
European legislation:
The European Charter for Regional and Minority Languages
Scottish Gaelic is covered under Part III of the European Charter for Regional and Minority Languages. Download the Council of Europe report 2013 about the United Kingdom or the UK report from 2018.
Framework Convention for the Protection of National Minorities
The Gaelic language is also covered by the Framework Convention for the Protection of National Minorities. You can read the latest reports of the UK and the Council of Europe here.
National legislation:
- names Gaelic an official language of Scotland;
- assigns to the Bòrd na Gàidhlig the responsibility to promote Gaelic, monitor its development, and to maintain a language plan.
- defines education a) in the use and understanding of; b) about; or c) by means of the Gaelic language3).
Every five years, Bòrd na Gàidhlig makes a National Gaelic Language Plan.
Education in practice
According to the census from 2011, 2500 children will be learning Gaelic in 2012 and 2013, opposed to 24 children in 1985.4). In 2007 MacCaluim (2007) estimated that about 700 learners obtained fluency.
For primary education, in 2018-2019 there are:
- 58 Gaelic Medium Education departments or dedicated schools total
- 7 dedicated Gaelic schools: 3 in Glasgow, and 1 in Inverness, Edinburgh, Lochaber, and Portree
- 3,457 pupils total attending Gaelic Medium Education5)
For secondary education, in 2018-2019 there are:
- 31 schools in Scotland which offer Gàidhlig for fluent speakers and/or other Gaelic medium subjects;
- 31 schools which offer Gaelic (Learners);
- the subjects English, French, Geography, History, Home Economics, Mathematics, Modern Studies, PE, Personal and Social Education, Religious Education, Science and Technology are taught at different levels through the medium of Gaelic6).
Learning resources and educational institutions
- Learn Gaelic Scot (different levels)
- Gaelic 4 Parents with games, stories, audio, homework help and more.
- Gealic in modern Scotland, an open course
- Fuaimean na Gàidhlig with sounds of Gealic
- An Drochaid with Gaelic audio with transcripts
- Tobar an Dualchais Kist O Riches with audio from 1930 on
Mercator's Regional Dossier
 Read more about Gaelic language education in Mercator's Regional Dossier (2018).
Read more about Gaelic language education in Mercator's Regional Dossier (2018).